The CAT4 Level D is designed for students typically in Year 7 in England or the final year of primary school in Ireland. This assessment provides schools with a clear baseline of how students think, learn, and approach problem-solving as they begin their secondary education.
I’m Liron Katz, and I’m here to help you approach CAT4 with clarity and give your child the tools to practise confidently with structured, free sample questions.
This page offers:
- Free Level D sample questions across all four CAT4 batteries
- Clear, step-by-step explanations for every answer
- A breakdown of Verbal, Quantitative, Non Verbal, and Spatial reasoning skills
- Focused study tips to improve accuracy, pacing, and confidence on test day
Use the links below to explore CAT4 Level D practice, guidance, and resources:
Free Practice Questions | CAT4 Level D Tips | Why Level D Matters | Understanding the Report | Learning Recommendations | Achievement Indicators | Prep Pack | FAQs
Free CAT4 Level D Sample Questions
This section introduces one sample question for each reasoning skill across all four CAT4 Level D batteries. These questions are designed to show your child what the questions look like and how to approach them confidently. Each sample question comes with a clear explanation of the thinking process as well as the correct answer.
Verbal Reasoning Battery
This battery contains two question types: Verbal Analogies and Verbal Classification
In Verbal Analogies, students identify the relationship between a pair of words and apply that same relationship to a new pair. A helpful strategy is to form a sentence that explains how the words are connected.
Lets take a look of the following analogy:
In Verbal Classification, students identify the word that shares a common category or defining feature with a group of related words.
Let’s try one together:
Quantitative Reasoning Battery
This battery includes two question types: Number Series and Number Analogies
The following example is a Number Series question. Number Series questions provide a series of numbers with a certain pattern or rule. You need to determine the pattern and use the rule to determine which number will come next in the series.
Let’s try one together:
In Number Analogies, students identify the relationship between pairs of numbers and apply that same relationship to complete a new pair. Let’s try one together:
Non-Verbal Reasoning Battery
This battery consists of two question types: Figure Matrices and Figure Classification
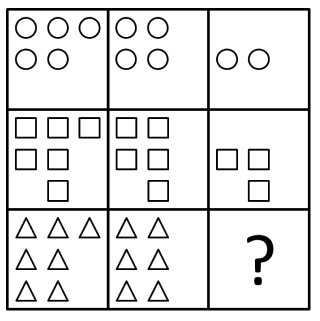
The following example is a Figure Matrix question.
In Figure Matrices, students complete a 2x2 or 3x3 grid by finding the image that follows the same visual rule across rows and columns.
Let’s try one together:
In Figure Classification, students identify the image that shares a common feature or relationship with a given set of images. Let’s try one together:
Spatial Ability Reasoning Battery
This battery includes two question types: Figure Analysis and Figure Recognition
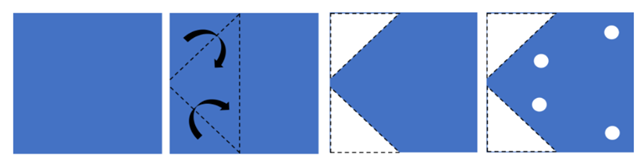
The following example is a Figure Analysis question. Figure Analysis questions show a paper folded several times and then punched with holes. The answer choices contain unfolded papers with punched-in holes. Students need to determine which of the answer choices is the final product of the unfolded punched-in paper.
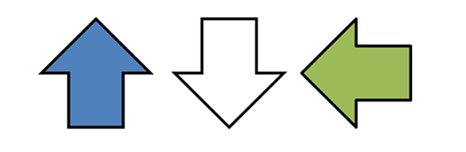
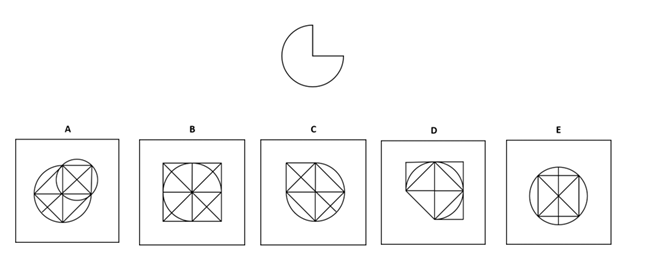
In Figure Recognition, students identify the option that contains the given shape in the same size and orientation. Let’s try one together:
Master the CAT4 Level D. Practice. Perform. Succeed.
CAT4 Level D Tips from Liron
Here are smart, student-friendly strategies for each CAT4 Level D question type.
The Special Role of CAT4 Level D: Tracking the Start of Secondary School Progress
CAT4 Level D acts as a vital bridge between primary and secondary education. Because students often move to larger schools with new teachers at this stage, the assessment provides an objective starting point. It is used to:
- Set a New Baseline: Establish a clear picture of a student’s reasoning abilities before they begin the secondary curriculum.
- Track Growth: Compare current scores with earlier CAT4 levels to see how cognitive skills are developing.
- Spot Hidden Potential: Identify gifted students or those with learning needs that might not be visible through standard classroom work.
- Guide Academic Placement: Help schools decide on initial "sets" or "streams" for subjects like Math and English.
What Is on Your Child’s CAT4 Level D Report
The CAT4 score report breaks down a child’s cognitive "toolkit" into four distinct areas, known as batteries. Understanding these helps parents see the "why" behind their child’s grades.
- Verbal Reasoning: The ability to understand ideas through words. This is essential for subjects like English, History, and Drama.
- Non-Verbal Reasoning: Solving problems using visual patterns and shapes. This indicates a child’s ability to think logically without needing language.
- Quantitative Reasoning: The ability to play with numbers and identify numerical relationships—the backbone of Mathematics and Economics.
- Spatial Ability: Visualizing 3D objects and rotating them in the mind. This is a massive indicator of success in STEM, Architecture, and Design & Technology.
- The Learning Profile: The report combines these scores to determine if a child has a "Verbal Bias," a "Spatial Bias," or a "Balanced Profile."
Personalized Learning Recommendations from the Report
One of the biggest advantages of the Level D report is the Personalized Learning Recommendations. By knowing how a child’s brain is wired, both teachers and parents can adapt their style:
- The Visual/Spatial Learner: These students often struggle with long lectures. They thrive when using mind maps, diagrams, and color-coded notes.
- The Verbal Learner: These students learn best through discussion, reading aloud, and written explanations. They often benefit from "teaching back" what they’ve learned.
- The Quantitative Learner: They prefer structure and logic. Breaking a complex task into a step-by-step sequence works best for them.
Achievement Indicators: What Level D Scores Suggest for Future Success
The Level D report includes Indicators of Achievement, which provide a statistical glimpse into the future. These are based on how thousands of previous students with the same cognitive profile performed in national exams like GCSEs or the Leaving Certificate.
- The "Most Likely" Grade: The result achieved by the majority of students with this profile.
- The "If Challenged" Grade: A higher target that represents what is possible if the student is highly motivated and well-supported.
These are guidelines, not destinies. A child’s final exam results are heavily influenced by their effort, the quality of teaching, their emotional well-being, and their study habits. The CAT4 tells you the capacity of the engine; the student still has to drive the car.
Preparing Your Child for CAT4 Level D Success with Our Test Prep Pack
Helping your child feel ready for CAT4 Level D does not have to be stressful. While the test measures reasoning ability, becoming familiar with the question formats builds confidence and improves performance.
The TestPrep Online Level D Preparation Pack gives you everything you need to support your child at home:
- 530+ practice questions across quizzes and full-length tests
- One CAT4 Study Guide explaining how to approach each question type
- One Score Guide to help you track progress clearly
- Unlimited retakes with six months of access
Give Your Child the Tools to Walk Into School Assessments Feeling Calm, Confident, and Ready to Succeed.
Ask Liron

A language and linguistics expert with an MA in Language Teaching and over a decade of experience developing assessment-aligned practice across multiple subjects that mirrors the rigor of real edtech tests. Liron creates prep packs with clear, structured exercises that enhance learning, adapt to digital tools, and empower every student to perform their best on a wide range of assessments
CAT4 Level D FAQs
Yes. While CAT4 measures reasoning ability, familiarity with question formats reduces anxiety and helps students demonstrate their true thinking skills.
According to GL Assessment, Level D is for students aged 10 years 6 months to 12 years 11 months, typically in Year 7, S1, or equivalent.
The pack includes 500+ questions, full tests, study and score guides, unlimited retakes, and 6 months of access.
Absolutely. Practice builds confidence, improves pacing, and helps students feel in control on test day.
Most families see strong results with 15–25 minutes a day over 2–3 months, making it easy to fit into busy school schedules.
Yes. Strong students benefit by learning how to approach unfamiliar question types efficiently and accurately.
The free questions provide a taste. The Prep Pack offers full coverage, deeper explanations, complete tests, and structured progression.
Practice does not change reasoning ability, but it improves performance by reducing errors, increasing speed, and boosting confidence.