Why TEAS Science Matters for Your Nursing Career
The TEAS Science section is often the most challenging part of the exam, but it's also your biggest opportunity to stand out. With 50 questions in 60 minutes, this section tests everything from human anatomy to chemistry - the foundation you'll need for nursing school success.
Free TEAS Science Practice Questions
Targeted practice is essential for the TEAS 7 Science section, which covers anatomy, chemistry, and scientific reasoning. Download our free TEAS 7 Science study guide PDF and practice questions to prepare effectively.
The Human Anatomy and Physiology section is the largest and most comprehensive part. It covers multiple body systems, including respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive, nervous, muscular, reproductive, integumentary, endocrine, urinary, immune, and skeletal systems.
Let's look at an Anatomy and Physiology question:
Anatomy and Physiology:
TEAS Science Sample Question 1 – skeletal system:
Which of the following is an irregularly shaped bone?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"When I teach skeletal anatomy, I tell my students to think about bone classification like sorting shapes. Long bones are like sticks (femur, fibula), flat bones are like plates (ribs, skull), and irregular bones are the unique puzzle pieces that don't fit standard categories. The sacrum is that triangular puzzle piece at the base of your spine - its weird shape is what makes it irregular. Always connect bone shape to its job!"
By including a substantial number of Anatomy and Physiology questions, the TEAS Test helps educational institutions assess candidates' preparedness for the scientific demands of healthcare programs and their potential for success in future clinical roles.
Improve Your TEAS Science Knowledge With Expert-Crafted Simulations in Our Test Prep Pack
Your reading comprehension is tested in the following question.
TEAS Science Sample Question 2 – Renal System:
Which of the following statements regarding glucose renal transport is incorrect?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I always tell my students: glucose is the kidney's VIP guest - it gets filtered but NEVER gets kicked out (secreted). The equation should be: Excretion = Filtration - Reabsorption. Period. No secretion for glucose! When you see glucose secretion in an answer choice, it's usually wrong. Remember: glucose is too valuable to waste."
In the next question, you must explain the physiological relevance of each factor. This question requires your ability to use English correctly.
TEAS Science Sample Question 3– Cardiovascular System:
Which of the following does not affect the binding affinity of oxygen to hemoglobin?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"Think of hemoglobin like a taxi driver - having more taxis (higher hemoglobin levels) means more total passengers (oxygen), but it doesn't change how eager each taxi is to pick up passengers (binding affinity). The driver's eagerness changes with road conditions (pH, temperature, CO2) but not with how many taxis are on the road."
This question is related to Anatomy and Physiology, specifically nutrition and the effects of vitamin deficiencies. It requires knowledge of common deficiency diseases and their associated vitamins
TEAS Science Sample Question 4-Common Deficiency Diseases
Which of the following diseases is caused by vitamin C deficiency?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I use the 'Sailor's Story' method: Scurvy = Sailors = Sea = vitamin C. Those old sailors couldn't get fresh citrus fruits, so they got scurvy. For the others: Rickets = kids with Rickets need vitamin D for strong bones, Beriberi = B1 deficiency. Create these memory hooks - they're lifesavers on test day!"
This question falls under Anatomy and Physiology, specifically the nervous system. It tests knowledge of the structure and function of neurons, including the role of the myelin sheath.
TEAS Science Sample Question 5-Nervous System
What is the primary role of the myelin sheath in the nervous system?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"Picture myelin as the insulation on electrical wires - but cooler! It doesn't just protect; it makes signals JUMP from gap to gap like a superhero leaping between buildings. This 'saltatory conduction' is why you can pull your hand away from a hot stove so fast. No myelin = slow reflexes = bad news for nurses!"
Ready to Master the TEAS Science Section?
Want more TEAS Science practice like these expertly crafted samples above? TestPrep-Online is the trusted leader in e-learning services, helping thousands of nursing students pass their education tests every year.
Chemistry:
TEAS Science Sample Question 6 - acids and bases:
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to acetic acid. Which of the following is expected to be the nature of the resulting solution?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"Here's my rule: Strong beats weak, every time. NaOH (strong base) + acetic acid (weak acid) = basic solution. Think of it like a boxing match - the strong base wins and the solution becomes basic. The salt formed (sodium acetate) also makes the solution basic through hydrolysis. Strong always dominates!"
Regular practice of scientific concepts, such as those covered in the TEAS test, can help reinforce your understanding and boost your TEAS test score by improving your ability to apply scientific principles to complex problems. Understanding chemical reactions is essential for providing safe, effective care and excelling in nursing education, including performing well on exams like the TEAS test.
TEAS Science Sample Question 7 – chemical reactions:
The proposed mechanism for the reaction A → D consists of 3 steps. The reaction profile diagram that describes this mechanism is given below:
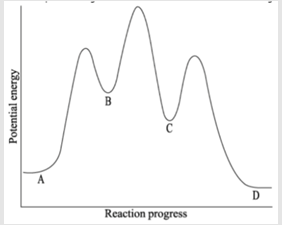
Which one of the following statements is true?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I teach my students the 'mountain hiking' method: peaks = transition states (the hard climbs), valleys = intermediates (rest stops). Count the peaks and valleys between start and finish. If you see 3 peaks (transitions) and 2 valleys (intermediates) between A and D, you've got your answer! Visual learners love this approach."
This question falls under Chemistry, specifically dealing with atomic structure and isotopes. It tests knowledge of atomic number, mass number, protons, and neutrons.
TEAS Science Sample Question 8-Atomic Structures
Which of the following correctly describes a property of carbon-14?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"Carbon is always carbon because it has 6 protons - that never changes! Carbon-14 means mass number 14. So: 14 (mass) - 6 (protons) = 8 neutrons. I tell students: 'The element name tells you the protons, the number after tells you the mass, subtract to get neutrons.' This formula works every single time!"
This is a Chemistry question focusing on chemical reactions and redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions. It requires understanding how to identify oxidation and reduction in a chemical equation.
TEAS Science Sample Question 9-Chemical Reactions
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Which of the following statements correctly describes the reaction above?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I teach OIL RIG religiously: Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain (of electrons). Mg goes from 0 to +2 (loses electrons = oxidized), H goes from +1 to 0 (gains electrons = reduced). Cl stays at -1 (spectator). Draw the charges above each element - visual tracking prevents mistakes!"
The next section of the TEAS Science test is about biology. Biology is a broad natural science that encompasses the study of all living organisms and their interactions with each other and their environments.
Biology:
TEAS Science Sample Question 10 – mitosis and meiosis
Which of the following occurs in mitosis but not in meiosis?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I use the 'family tree' analogy: Mitosis = identical twins (2 identical cells), Meiosis = diverse siblings (4 different gametes). Mitosis is 'copy-paste' - one division, two identical cells. Meiosis is 'mix-and-match' - two divisions, four unique cells. The question asks what's unique to mitosis - that's the single division!"
Knowledge of cellular biology enables nurses to provide more effective care across various aspects of health, from wound healing and infection control to comprehending genetic conditions. This ultimately enhances their ability to interpret patient conditions and deliver informed, high-quality nursing care.
TEAS Science Sample Question 11 – cellular biology:
Which of the following is characteristic only to eukaryotes and not to prokaryotes?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"Remember: prokaryotes are 'pro' (before) having organized stuff. They don't have a nucleus, so they don't need histones to package DNA. Eukaryotes have a nucleus and need histones to organize their DNA like filing cabinets. Everything else on this list? Both cell types have it. When in doubt, think 'nucleus = eukaryote only' features!"
This question is related to Biology, specifically cell biology and organelles. It requires knowledge of the function of ribosomes in protein synthesis.
TEAS Science Sample Question 12-Cell Biology and Organelles.
What is the main function of ribosomes in a eukaryotic cell?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I teach students to identify variables like this: Independent = what researchers CHANGE (treatment type), Dependent = what they MEASURE (blood pressure change). Control group = no treatment baseline. The placebo group (sugar pill) tests psychological effects, not the old drug group. Draw it out: treatment → blood pressure change. This visual helps every time!"
Prepare For The TEAS Test
While the TEAS Science exam may be the largest component of the TEAS exam, it is certainly not the only one. Our experts at TestPrep-Online have compiled a comprehensive preparation course for all of the TEAS sections, which includes full TEAS Science Practice tests and a comprehensive set of study guides so you can better understand what the test includes.
Let's continue to the scientific reasoning question type covered in this TEAS Science Free Practice Test. As nursing students, you'll encounter complex medical situations that require more than just memorization of facts. Scientific reasoning is a critical skill that will serve you well in your nursing career, enabling you to analyze data, evaluate evidence, and make informed decisions.
Scientific Reasoning:
TEAS Science Sample Question 13 – the scientific method:
Scientists experimented to examine whether a new medicine they developed for reducing blood pressure is better than an old medicine that already exists in the market.
They divided their participants into four groups: the first group took the new medicine, the second group took the old medicine, the third group took a pill without any active ingredient, and the fourth group received no treatment.
The blood pressure of the four groups was measured before the treatment and again after two weeks of treatment, and the difference was calculated for each group.
Which statements regarding the experiment are true?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I teach my nursing students this simple formula: Independent = what you control, Dependent = what you measure. In medication studies, the drug type is independent, patient outcomes are dependent. Control groups get no treatment, placebo groups get fake pills. Quick check: Can the researcher change it? That's independent. Does it respond to treatment? That's dependent."
While the TEAS Science section primarily focuses on scientific knowledge and reasoning, having a solid foundation in certain math skills can help you better understand and solve science-related problems. The emphasis is on applying these math skills in scientific contexts rather than pure mathematical calculations. Take our free TEAS Math Test and see if your skills are college-ready.
TEAS Science Sample Question 14 – measurements and tools:
During a lab lesson, a chemistry student was asked to transfer exactly 2 milliliters of a solution from a test tube that contains 20 milliliters of the solution to another test tube. Which of the following tools should the student use?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"I tell my students: match the tool to the job's precision needs. For small, precise volumes (like medications!), use a volumetric pipette. Graduated cylinders are for 'ballpark' measurements, thermometers measure temperature, meter sticks measure length. In nursing, precision matters - you wouldn't estimate a medication dose, right? Same principle here!"
TEAS Science Sample Question 15
A farmer needs to calculate how much feed to buy each week for his farm. He knows that each cow eats 24 pounds of feed a day and each pig eats 7 pounds of feed a day. If he has x cows and y pigs, how much feed does he need to buy each week?
TestPrep-Online Tutor's Tip:
"My Two-Step Method:
- Step 1: Calculate daily total (24x + 7y).
- Step 2: Multiply by 7 for weekly (168x + 49y). Think medication dosing: daily dose × 7 days = weekly supply.
Never skip the daily calculation - it prevents errors just like double-checking medication math prevents dosing mistakes."
Practice for the TEAS Science Test
Preparing for the TEAS Science test is essential for success in your nursing or allied health career path.
- To excel in this section, focus on understanding key concepts in anatomy, physiology, biology, and chemistry.
- Practice interpreting scientific data, understanding scientific method applications, and identifying basic scientific principles.
- Regular practice with TEAS-style questions will help familiarize you with the test format and improve your confidence in tackling challenging topics.
- Dedicate time to review foundational knowledge and work through practice tests to ensure you're well-prepared for the TEAS Science test.
Embrace Your TEAS Exam Preparation Journey
Remember, each moment you spend preparing for the TEAS exam is an investment in your future as a compassionate and capable nurse. Embrace the journey, enjoy the learning process, and trust in your abilities.
FAQs About TEAS Science
Most successful students spend 4-6 weeks preparing, with 1-2 hours daily focused on science topics. Our prep pack includes a personalized study schedule to optimize your preparation time.
Yes, but policies vary by school. Most allow retakes after 30-45 days. Don't risk it - prepare thoroughly with our proven system the first time.
All materials are updated for TEAS 7 (current version). We regularly refresh content to match the latest exam format and difficulty level.



