Schools throughout the UK and Ireland administer the GL Assessment Cognitive Abilities Test fourth edition (CAT4) to recognize students’ academic levels and needs. High scores on the CAT4 are also often used to identify children who qualify for gifted & talented programs and is also used as a private school entrance test.
Learn more about the benefits of taking the CAT4 test and discover how TestPrep-Online can help your child prepare for the day of the test.
- CAT4 Level X & Y — Year 2 & 3
- CAT4 Level A - Year 4
- CAT4 Level B - Year 5
- CAT4 Level C - Year 6
- CAT4 Level D - Year 7
- CAT4 Level E - Year 8
- CAT4 Level F - Year 9 & 10
- CAT4 Level G - Year 11+
What Are CAT4 Questions and How Do They Help?
Practicing for the CAT4 strengthens core cognitive abilities like verbal, non-verbal, quantitative, and spatial reasoning by engaging the brain in diverse problem-solving. This targeted cognitive exercise helps maintain and improve mental acuity, directly combating "summer slide" by keeping minds active and ready for the next academic year.
Free CAT4 Test Practice Questions
Do you live in Germany? Access our CAT4 Test PrepPack through Jobtestprep Germany.
What is the Verbal Reasoning Battery?
The Verbal Reasoning battery includes two subsections - Verbal Classification and Verbal Analogies.
Verbal Classification
Questions present three words, and five answer choices. The student must choose the word from the answer choices with the same meaning as the three given words.
Verbal Analogy
Questions present students with three words in the format of “A → B : C→ ____”, with A, B and C representing given words.
In each question, the words A and B relate to each other in a specific way. Student must identify this relation, and apply it to word C by selecting the fourth word from five given answer choices that is best suited.
Unlike many other forms of gifted and talented testing, the CAT4 exam does not focus on either reading skills or vocabulary use but rather the student’s ability to demonstrate reasoning skills through the use of words.
What is the Quantitative Reasoning Battery?
The Quantitative Reasoning Battery is comprised of Number Analogy questions and Number Series questions. It requires basic arithmetical skills and relies on minimal mathematical knowledge. This battery aims to assess pupils’ skill to find mathematical relations between numbers, in a similar way as the Verbal Reasoning Battery.
Number Analogy
Questions, like Verbal Analogy questions, are presented in the format of “A → B : C→ ____”. Although, in this case, A, B and C are given numbers. The first two numbers (A and B) share a mathematical connection. The student must deduce that connection and find an answer choice, out of the five given numbers, which shares the same connection with the third number presented (C).
Number Series
Questions present a series of numbers with a certain progression rule. The student must figure out the rule and choose an answer choice, out of five given options, which fits the same rule as the last number of the series.
What is the Non-verbal Reasoning Battery?
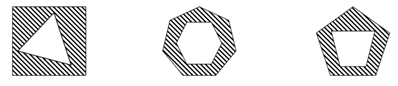
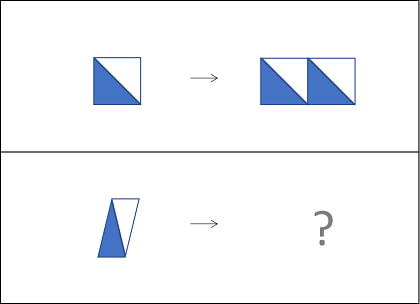
The Non-Verbal Reasoning Battery questions use shapes, other than words or numbers, to measure students’ ability to reason and think with non-verbal material, such as shapes or matrices. This battery is split into Figure Classification questions and Figure Matrices questions.
Figure Classification
Questions require recognizing a connection among three given shapes and choosing one of the five answer choices that shares that connection. The connection can be a conceptual link or a shared characteristic that the given shapes have in common.
Figure Matrices
questions present a matrix comprised of four boxes. Each of the two boxes in the top row contains a shape, while only the first box in the bottom row is filled. The fourth is left empty. The boxes in the top row share a connection, which the students are asked to recognize and apply to the in the bottom row by choosing the correct answer choice to fill the empty box.
What is the Spatial Ability Battery?
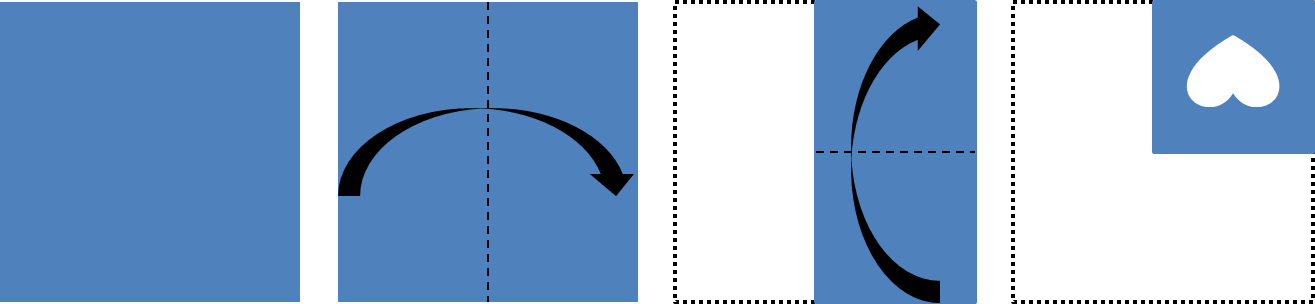
The Spatial Ability Battery assesses the pupils’ ability to hold an image in their mind and manipulate it. It has Figure Analysis and Figure Recognition questions.
Figure Analysis
Questions show pictures depicting paper folded several times and then punched with holes. The five answer choices contain unfolded papers with punched holes. The student is asked to determine which of the answer choices is the final product of the folding in the pictures.
Figure Recognition
Questions present a singular shape. The answer choices are five complex designs. The students must identify which answer choice contains the presented shape (the same size and features).
Boost Your CAT4 Scores!
TestPrep-Online's complete CAT4 Preparation Packs include
Tutorials, CAT4 Practice Tests, and Expert Tips from $69
Free CAT4 Practice Test PDF
View and download free CAT4 Sample Papers. This printable practice test includes sample questions from all the various question types in the actual CAT4 (Quantitative Reasoning, Verbal Reasoning, Non Verbal Reasoning and Spatial Reasoning) along with elaborated solutions and thorough explanations. Solving this sample test is an excellent starting point for preparing for the upcoming CAT4 exam.
The CAT4 test is the UK’s most widely used reasoning ability assessment, designed to help schools with grade placement decisions and to track the development of students' cognitive abilities over time—both in UK schools and in international schools around the world.
CAT4 Test FAQs
The CAT4 test is the UK & Ireland most widely used reasoning ability assessment test, designed to help schools understand students' abilities and develop them. It is administered throughout the UK and Ireland and by many international schools worldwide to students aged 6 to 17.
Developed and delivered by GL-Assessment, based on years of thorough research, this edition of the CAT4 test helps identify individual students' strengths and weaknesses while also monitoring the performance of groups of students.
It is designed to measure cognitive reasoning skills while demanding little reading comprehension and arithmetical skills, thus making the test less biased towards native speakers. Cronbach's Alpha formula confirmed the CAT4's reliability.
If you are a teacher or tutor, we recommend checking out this page!
Or learn everything you need to know about homeschooling.
A "good" Cognitive Abilities Test CAT4 score is subjective and depends on the context in which the test is being used, including the specific goals for assessment and the benchmarks set by the school or educational authority. The CAT4 test results are typically reported as Standard Age Scores (SAS), percentile ranks, and stanines, providing a comprehensive view of a student ability relative to others of the same age.
Here's a brief overview of how to interpret these scores:
- Standard Age Scores (SAS): The average score is set at 100, with most students scoring between 85 and 115. Scores above 115 are considered above average, and scores below 85 are considered below average.
- Percentile Ranks: These indicate the percentage of students in the norm group who scored below a particular student. For example, a percentile rank of 70 means the student scored better than 70% of students in the norm group.
- Stanines: These are derived from percentile ranks and range from 1 to 9, with 5 being average. Scores of 7 to 9 are considered above average, 4 to 6 are average, and 1 to 3 are below average.
In general, a "good" CAT4 test score might be considered one that falls within the above-average range (SAS above 115, percentile ranks above 75, stanines 7-9).
The Cognitive Abilities Test CAT4 is designed to measure cognitive abilities, not academic achievement, so it's challenging in the sense that it tests reasoning skills in various areas. However, since it assesses inherent abilities rather than learned knowledge, it's not "hard" in the traditional sense of requiring study or memorization. Some students might find certain sections more difficult based on their individual strengths and weaknesses.
GL-Assessment administers the CAT4 test in 10 different test levels, with each level aimed at other age groups. The following table presents all test levels and their matching target year group and age range:
CAT4 Level | England & Wales | Scotland | Northern Ireland | Ireland | Age Range |
Year 2 | Primary 3 | Y3 (P3) | 1st class | 6 – 8 | |
Y | Year 3 | Primary 4 | Y4 (P4) | 2nd class | 7 – 9 |
Pre-A | Year 3 | Primary 4 | Y4 (P4) | 2nd class | 6.5 – 9 |
Year 4 | Primary 5 | Y5 (P5) | 3rd class | 7.5 – 10 | |
Year 5 | Primary 6 | Y6 (P6) | 4th class | 8.5 – 11 | |
Year 6 | Primary 7 | Y7 (P7) | 5th class | 9.5 – 12 | |
Year 7 | Secondary 1 | Y8 (F1) | End of 5th class/6th class | 10.5 – 13 | |
Year 8 | Secondary 2 | Y9 (F2) | End of 6th class/1st Year | 11.5 – 14 | |
Year 9 & 10 | Secondary 3 & 4 | Y10 & Y11 (F3 & F4) | 2nd and 3rd Year | 12.5 – 16 | |
Year 11+ | Secondary 5 & 6 | Y12+ (F5+) | 4th/TY/5th class | 14.5 – 17+ |
Except for the three lowest test levels (X, Y, & Pre-A), which are designed for very young children and thus administered in a different format and structure, the content of each of the higher levels (A to G) is similar in terms of format and question types. The main distinction between them is in their increasing difficulty level, which corresponds to the overlapping configuration of target year groups.
GL Assessment's CAT4 test has both paper-based and computer-based versions; each takes approximately two hours to complete. The primary test levels (A-G) have four different batteries, with each containing two subsections.
The test is administered in three parts, each divided into two or three short tests:
Sub-Test | Number of Questions | Test Time |
Part 1 | ||
Figure Classification | 24 questions | 10 minutes |
Figure Matrices | 24 questions | 10 minutes |
Part 2 | ||
Verbal Classification | 24 questions | 8 minutes |
Verbal Analogies | 24 questions | 8 minutes |
Number Analogies | 18 questions | 10 minutes |
Part 3 | ||
Number Series | 18 questions | 8 minutes |
Figure Analysis | 18 questions | 9 minutes |
Figure Recognition | 18 questions | 9 minutes |
Students are allowed to solve the questions from the same battery in any order they'd like but can only answer questions from one battery at a time.
Schools use the CAT4 to adjust the learning experience to student-group and individual needs. As a result, teachers gain insight into subjects that students find difficult and can adequately support them. Moreover, CAT4 exam questions require reasoning skills other than relying on mathematical or verbal solid skills, thus allowing students with a language barrier or dyslexia to do well.
CAT4, as the name suggests, is a cognitive test, and as such, it measures skills that are also being tested in gifted children's programs. The informative reports help teachers identify those talented children and support their studying in an environment that will further foster their abilities.
An additional value the CAT4 has is identifying students who are having difficulties. Due to its unique structure, students who receive low scores in the CAT4 reports often do so for a reason. For example, the reports allow the teachers to check if the child randomly guessed questions or had difficulty with a specific subject.
As in many cognitive assessments, the CAT4 Test has specific recurring patterns, and getting familiar with these patterns increases the chances to score higher.
In addition to getting familiar with the test's patterns, enriching vocabulary can help score high on the verbal analogies and verbal classification sections. Moreover, enriching your vocabulary is possible within a relatively short time and can even be fun.
Lastly, remember that the test day is usually accompanied by anxiety, impacting the student's performance on the test. Getting familiar with the CAT4's content and format and practicing under the same time limit as in the real test is likely to reduce anxiety and impact the student's performance. Hence, the results of the test will more accurately reflect the ability of the student.
Practicing with CAT4 Practice Tests and explanations allows students to familiarize themselves with the test and gives them the confidence to succeed. Properly preparing also has the advantage of recognizing strengths and weaknesses and functioning without stress under time constraints.