The CAT4 (Cognitive Abilities Test) is a reasoning-based assessment that schools use to understand how your child learns and where they’re likely to succeed academically.
I’m Liron Katz, a CAT4 preparation expert, and I’ve spent years building targeted materials that help students perform at their best on this test.
This page gives you exactly what you need to start preparing with confidence, including:
- CAT4-style practice questions with clear explanations
- A simple overview of the test structure and skill areas
- Score insights and how schools use CAT4 results
- Practical guidance and parent-focused tips
Explore free CAT4 practice questions now:
Verbal Analogies | Verbal Classification | Number Analogies | Number Series | Figure Matrices | Figure Classification | Figure Analysis | Figure Recognition
Free CAT4 Test Practice Questions
Below are sample questions from all 8 CAT4 sub-tests. They are taken from different grade levels.
What is the Verbal Reasoning Battery?
The Verbal Reasoning Battery measures how well students understand and use language skills that are essential for reading comprehension, clear writing, and following complex instructions. In the CAT4, these abilities are tested through two types of questions:
- Verbal Analogies
- Verbal Classification
Verbal Analogies Sample Question:
In the Verbal Analogies questions, you are given a pair of words that share a specific relationship. This is followed by a first word of a second pair. You must choose the word that completes the second pair so that it shares the same relationship as the first.
Each question presents five answer options, but only one is correct. Sounds tricky? Don’t worry, we’ll break it down together.
Verbal Classification Sample Question
In the Verbal Classification questions, you are given three words that belong to a specific group or share a common trait. You must identify the connection between them and choose the one word from the answer options that belongs in that same group.
It might seem puzzling at first, but once you know what to look for, it gets much easier.
Like These Sample Questions- Why Not Find More Samples Selected By Grade Level
What is the Quantitative Reasoning Battery?
The Quantitative Reasoning Battery measures how well students can recognise numerical patterns and logical relationships, skills that form the foundation of problem-solving in mathematics and science. In the CAT4, these abilities are assessed through two types of questions:
- Number Analogies
- Number Series
Number Analogy Sample Question
In the Number Analogies questions, you are given two pairs of numbers that follow the same mathematical rule. You must identify this rule and apply it to a third pair to find the missing number. The rule may involve addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, or a combination of these.
Number Series Sample Question
In the Number Series questions, you are given a sequence of numbers that follow a specific mathematical pattern. You must determine the rule (e.g., alternating operations or progressive changes) to identify the next number in the series.
What is the Non-Verbal Reasoning Battery?
The Non-Verbal Reasoning Battery measures how well students can identify patterns and relationships in shapes and visual information, skills that are valuable for mathematics, coding, and interpreting diagrams. In the CAT4, these skills are assessed through two types of questions:
- Figure Classification
- Figure Matrices
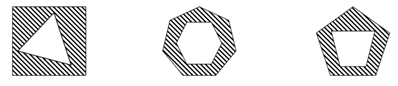
Figure Classification Sample Question
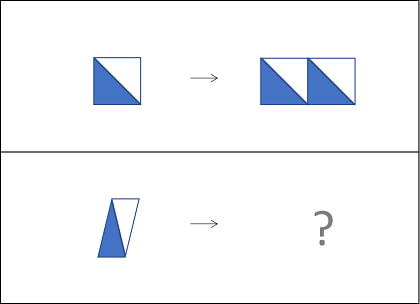
In Figure Classification, you are presented with three shapes that share a common visual characteristic or rule. You must identify this connection and choose the answer option that follows the same rule to join the group.
Figure Matrices Sample Question
In the Figure Matrix, you are given a grid (2x2 or 3x3) where the shapes change according to specific rules across rows or down columns. These changes may involve rotation, reflection, or movement of parts. You must identify the logic to find the missing figure that completes the matrix.
What is the Spatial Ability Battery?
The Spatial Ability Battery measures how well students can mentally visualise and manipulate shapes, skills that are important for geometry, design tasks, and understanding technical concepts. In the CAT4, these abilities are assessed through two types of questions:
- Figure Analysis
- Figure Recognition
Figure Analysis Sample Question
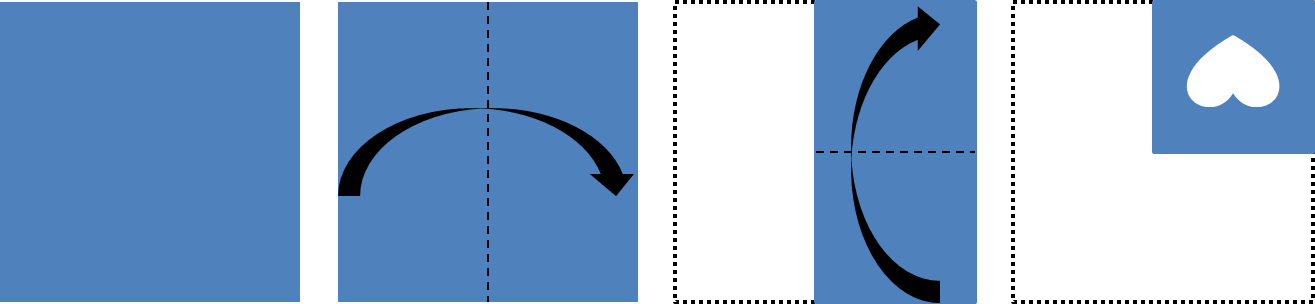
Figure Analysis questions show a square piece of paper being folded several times and then punched with holes or shapes. The answer choices show the paper completely unfolded. You must choose the design that correctly shows where the holes would appear after the paper is unfolded, following the rules of symmetry.
Figure Recognition Sample Question
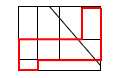
Figure Recognition questions show a specific target shape on the left and five complex designs on the right. You must identify which of the five designs (A, B, C, D, or E) contains the exact same target shape. The shape must be hidden within the lines of the design in the same size and orientation, with every side of the target shape shown in full.
Boost Your CAT4 Scores!
TestPrep-Online's complete CAT4 Preparation Packs include
Tutorials, CAT4 Practice Tests, and Expert Tips from $69
What Is the CAT4?
The CAT4 is a widely used reasoning ability assessment developed by GL Assessment. Schools use it to support placement decisions and to understand how students think and learn over time. It is used in both UK and international schools. The CAT4 is:
- Computer based
- Strictly timed
- Designed to measure reasoning ability, not taught curriculum content
It assesses four key reasoning areas (called batteries), each with two sub-tests:
Verbal Ability Reasoning
Verbal Classification
Verbal Analogies
Quantitative Reasoning
Number Analogies
Number Series
Non-Verbal Reasoning
Figure Classification
Figure Matrices
Spatial Ability Reasoning
Figure Analysis
Figure Recognition
How Is the CAT4 Administered?
The CAT4 is made up of short, strictly timed sections. Students cannot return to previous questions once time runs out, which is why time management and familiarity with the format are essential.
|
Part 1 |
Figures & Verbal Reasoning |
25–30 Minutes |
|
Part 2 |
Numbers & Shapes |
20–30 Minutes |
|
— |
— |
— |
|
Total |
Two Parts |
45–60 Minutes |
|
CAT4 Section |
Number of Questions |
Test Time |
|
Part 1 |
|
|
|
Figure Classification |
24 Questions |
10 Minutes |
|
Figure Matrices |
24 Questions |
10 Minutes |
|
Part 2 |
|
|
|
Verbal Classification |
24 Questions |
8 Minutes |
|
Verbal Analogies |
24 Questions |
8 Minutes |
|
Number Analogies |
18 Questions |
10 Minutes |
|
Part 3 |
|
|
|
Number Series |
18 Questions |
8 Minutes |
|
Figure Analysis |
18 Questions |
9 Minutes |
|
Figure Recognition |
18 Questions |
9 Minutes |
|
— |
— |
— |
|
Total |
168 Questions |
~2 Hours |
Watch the CAT4 Explained in Under 5 Minutes
Why Schools Use CAT4 (And What Parents Aren’t Told)
CAT4 scores help:
- Predict academic growth
- Determine placement and eligibility for gifted programmes
- Identify potential across different educational backgrounds
But what parents often aren’t told is CAT4 provides a picture of how a child thinks, rather than what they have been taught.
Why Even High-Achieving Students Benefit from Preparation
The CAT4 is a stimulating mental workout, a challenging test that engages students in different types of thinking and problem-solving. With the right preparation, they can approach its unique features with skill and confidence.
Because it’s different from most classroom tests, some parts may take a little time to get used to. Common features include:
- Fast Timing: Each sub-test lasts just 8–10 minutes, requiring quick thinking and clear decision-making without second-guessing and with no chance to go back once the time is up.
- Cognitive Switching: Transitioning from a challenging word puzzle to a rapid number pattern and then to a spatial reasoning task in just minutes requires mental agility.
- Unfamiliar Formats: The test uses layouts and question types that students don’t often see in school, from 3-D rotations to symbolic sequences.
- No Memorization: Success depends on flexible problem-solving and strategic thinking rather than recalling facts or formulas.
Understanding CAT4 Scores for Parents
These boxes show the key components that make up your child’s CAT4 score.
Standard Age Score (SAS)
Compares your child’s performance to others of the same age. An SAS of 100 is average, while 120+ indicates strong performance that schools may use when considering enrichment opportunities.
National Percentile Rank (NPR)
Shows the percentage of students your child outperformed nationally. For example, an NPR of 80 means your child scored higher than 80% of peers their age.
Group Rank
Compares your child’s performance to classmates or peers in the same school, helping teachers spot learning needs quickly.
Stanine
A simple 1–9 scale used by schools to group students for instruction. Higher stanines can open doors to advanced programmes.
The CAT4 Student Profile (Learning Style)
CAT4 also produces a student profile based on patterns across the four reasoning areas.
This profile reflects how a child is most likely to learn best based on their cognitive strengths, not how they currently perform in class.
Verbal and spatial reasoning are treated as two ends of a continuum, with numerical and nonverbal reasoning sitting between them. Using stanines and overall performance, students are placed into one of seven profiles, which helps identify whether a child may naturally prefer.
These profiles show whether a child naturally prefers learning through words or through visuals and patterns.
-
Verbal bias means the child is stronger in language-based thinking like reading, writing, and discussion.
-
Spatial bias means the child is stronger in visual thinking like diagrams, shapes, and hands-on problem solving.
-
No bias means the child shows a balanced mix of both.
The strength of the bias, from mild to extreme, shows how strong that preference is.
What Happens After Your Child Takes the CAT4?
Many parents wonder what comes next after test day. The good news? You play an active role in turning CAT4 results into meaningful support for your child. Here's your roadmap:
Expect results soon: Most schools share CAT4 results within two to three weeks and may arrange a meeting to discuss what the findings mean for your child’s learning plan.
Review together: Go over the report with your child’s teacher and ask how it will be combined with classroom work, other assessments, and your child’s interests.
Ensure a full picture: This collaborative approach helps make sure plans for support, enrichment, or placement reflect your child’s abilities in full.
Use the insights: Celebrate strengths, guide learning at home, and work with teachers on strategies to keep your child progressing with confidence.
How Our CAT4 Test Prep Helps
We turn test-day stress into readiness. Our prep pack includes:
- Full-Length Practice Tests: Give students a realistic preview of the CAT4, so they know exactly what to expect on test day.
- Timed Sub-Tests: Teach students to manage strict CAT4 time limits without rushing into mistakes.
- Step-by-Step Explanations: Clarify why each answer is correct, building transferable reasoning skills.
- Targeted Reasoning Drills: Strengthen specific verbal, non-verbal, quantitative, and spatial skills.
- Strategy Tips: Equip students with proven methods for tackling tricky question types.
- Progress Tracking: Show growth clearly and highlight where further practice is needed most.
Students who use our prep materials report feeling significantly more confident and prepared on test day, with many seeing score improvements of 10-15 points in their target areas.
Get Started with Confidence
Ready to give your child the advantage of knowing the CAT4 inside-out before test day?
Want to see what our CAT4 tests looks like- here is a mini version of our CAT4 Test:
Ask Liron

A language and linguistics expert with an MA in Language Teaching and over a decade of experience developing assessment-aligned practice across multiple subjects that mirrors the rigor of real edtech tests. Liron creates prep packs with clear, structured exercises that enhance learning, adapt to digital tools, and empower every student to perform their best on a wide range of assessments
CAT4 Test FAQs
CAT4 measures how your child thinks, not what they’ve memorized. It assesses reasoning skills across verbal, quantitative, non-verbal, and spatial areas to help schools understand learning potential and academic strengths.
Schools use CAT4 to predict academic progress, guide placement decisions, and identify gifted potential because it provides insight into a child’s learning style rather than just current classroom performance.
Yes. While CAT4 isn’t curriculum-based, familiarity with question formats and timing significantly improves confidence, speed, and accuracy, helping students perform closer to their true ability level.
Absolutely. CAT4 is designed to be fair across school systems and learning experiences, making it especially valuable for students from international, independent, or non-traditional educational settings.
The test is computer-based and strictly timed, with short sub-tests lasting about 8–10 minutes each. Students cannot return to previous questions, which makes time management and practice essential.
Scores include Standard Age Scores (SAS) and National Percentile Ranks (NPR), which show how your child compares to others their age. These results help schools plan support, enrichment, or academic pathways.
The student profile shows whether your child has a verbal, spatial, or balanced learning preference, helping teachers and parents tailor teaching methods and learning strategies more effectively.
Our Prep Pack provides full-length timed tests, detailed explanations, strategy tips, and progress tracking, giving your child structured, realistic practice that free samples alone cannot offer.